The machine that started out printing tiny models is now printing entire buildings. 3D printing is changing the building process for construction companies around the world and opening up new opportunities for change and innovation.
What is 3D Printing?
3D printing is a process of manufacturing physical objects based on digital designs in which a computer-controlled machine lays material down layer by layer to create the object. Objects can be 3D printed in polymer (i.e. plastic), metal, ceramic, mortar, or concrete. The most common material used for 3D printing in construction is concrete. Large-scale printers use a special concrete-composite mixture (making it thicker than normal concrete) that allows the layers to dry and remain self-supporting as they set.
How 3D Printing is Used in Construction
3D printing has been used in the construction industry for decades to create prototypes and three-dimensional models to show clients before beginning the construction process. But now 3D printing is going beyond the planning phase as companies are starting to 3D print everything from small parts of buildings up to entire homes.
You might also like: Technology’s Effect on Safety Protocol After a Pandemic
Building components can be prefabricated by a 3D printer off-site, then transported and assembled at the building location for faster, more efficient assembly. This is the most common 3D printing method used in commercial construction, allowing construction companies to create more customizable design shapes and building segments in large scale construction jobs in less time for less money. The prefabrication method saves construction companies 50-70% on construction time, 50-80% on labor costs, and 30-60% on material costs — all of which greatly reduce building costs.
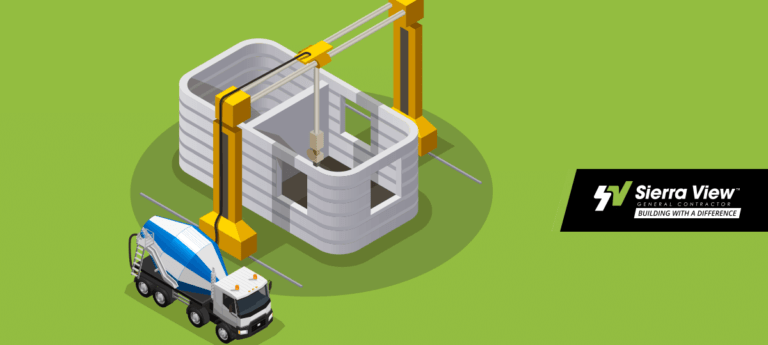
If the construction company has a large enough, portable printer, the entire house or small commercial building can be 3D printed directly on-site. Most of these completely 3D printed structures are currently limited to small-scale, single-story buildings and homes. However as the technology continues to advance, future 3D printed buildings may not be limited by their size.
Pros & Cons
3D printing is used for a wide range of applications in the construction industry because it is versatile, fast, inexpensive, automated, and allows for custom, complex designs. However, there are drawbacks to this new technology that can make current 3D printed construction challenging.
Saves Time and Money on a Construction Site
A traditional construction task that takes two weeks can be reduced to just three or four days by a 3D printers’ ability to work quickly and without error around the clock. They reduce human physical labor and, by extension, labor costs. With machines performing most of the heavy lifting jobs, not only are costs cut, but the risk of injury is reduced for construction workers as well.
Also read: From Sustainable to Regenerative Building
3D printing is also more sustainable and eco-friendly than traditional construction methods. 3D printers reduce construction waste by only using the exact amount of raw materials that are needed and by allowing up to 50% of those materials to be made from recycled building materials.
Requires Higher Equipment Cost
While 3D printing can reduce material costs in the long run, they require a much higher equipment cost upfront. A standard onsite 3D printer can cost anywhere from $500,000 to $2 million and is only capable of printing small buildings.
Larger construction jobs would require multiple printers with advanced features to get the job done. Transporting and setting up the printer can be expensive as well, which can detract from the savings in material cost. One of the biggest challenges of 3D printed construction is that outdoor construction sites are generally subject to erratic weather changes that can affect the cooling/setting conditions of the layers of material and impact the structural stability of the building.
These aspects can make 3D printing less viable for some construction workers today, however with the technological evolutions that 3D printing has and continues to experience, these challenges may cease to be problematic someday soon.
The Future of 3D Printing
With advancements in the 3D printing market and technology, large-scale commercial buildings could be entirely 3D printed in the future. Once standardized 3D printing construction codes have been determined and implemented and the printers have been able to overcome their size and speed limitations, 3D printing has the potential to become a massive player in the construction industry and change the way that future buildings are designed and created.